TECHNOLOGY
Dentistry has experienced remarkable progress through technological innovations in recent years, enhancing patient experiences, diagnostic precision, and treatment efficiency. Key technological advancements in dentistry include:
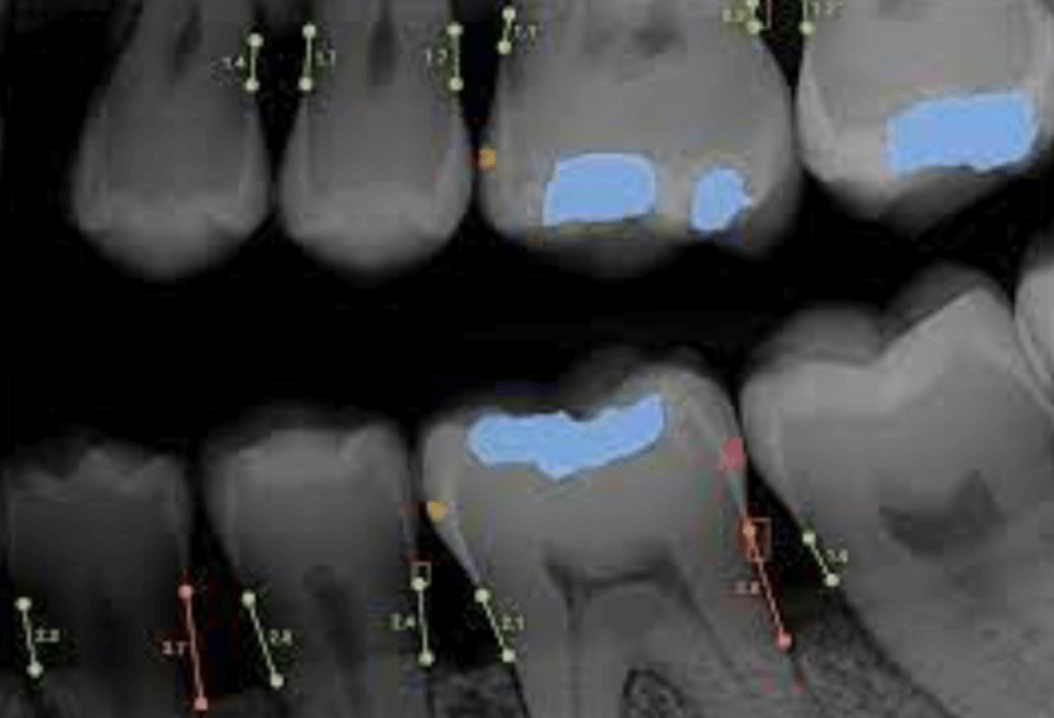
Radiography:
Digital X-rays have revolutionized dental imaging by replacing traditional film-based methods. They offer lower radiation exposure, quicker image processing, and advanced features like image enhancement and manipulation, enabling more accurate diagnostics.
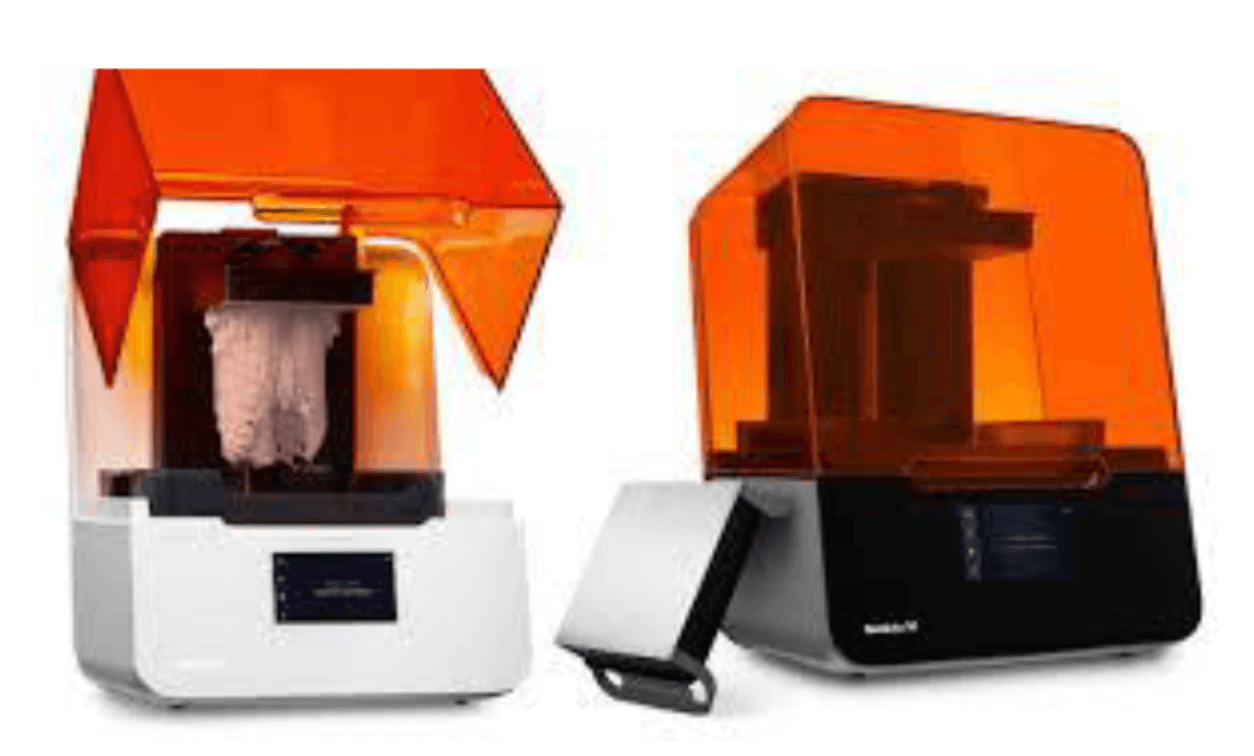
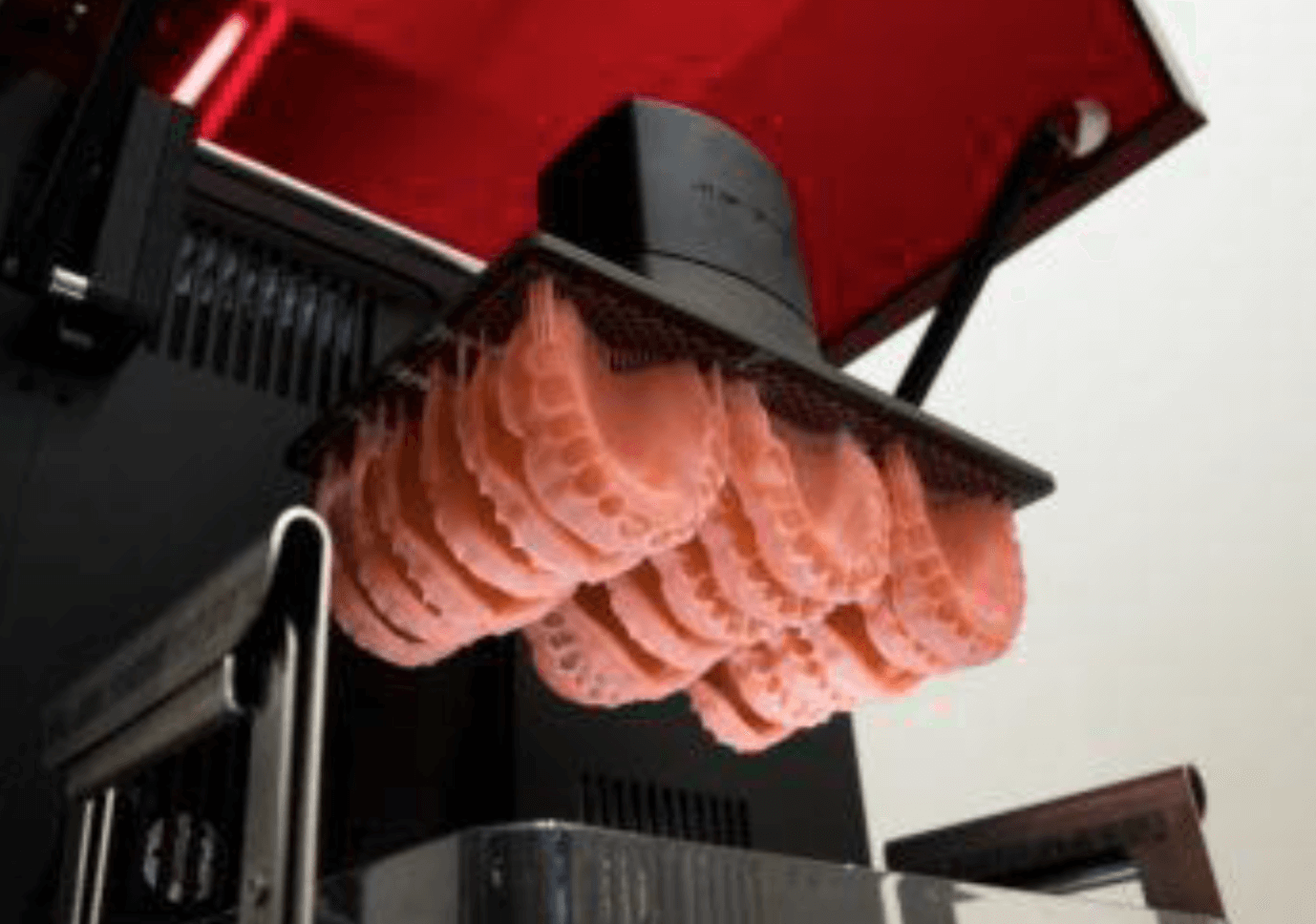
Printing:
3D printing has transformed dentistry by facilitating the production of custom dental implants, crowns, bridges, and orthodontic devices. This technology ensures highly accurate, patient-specific solutions for improved treatment outcomes.
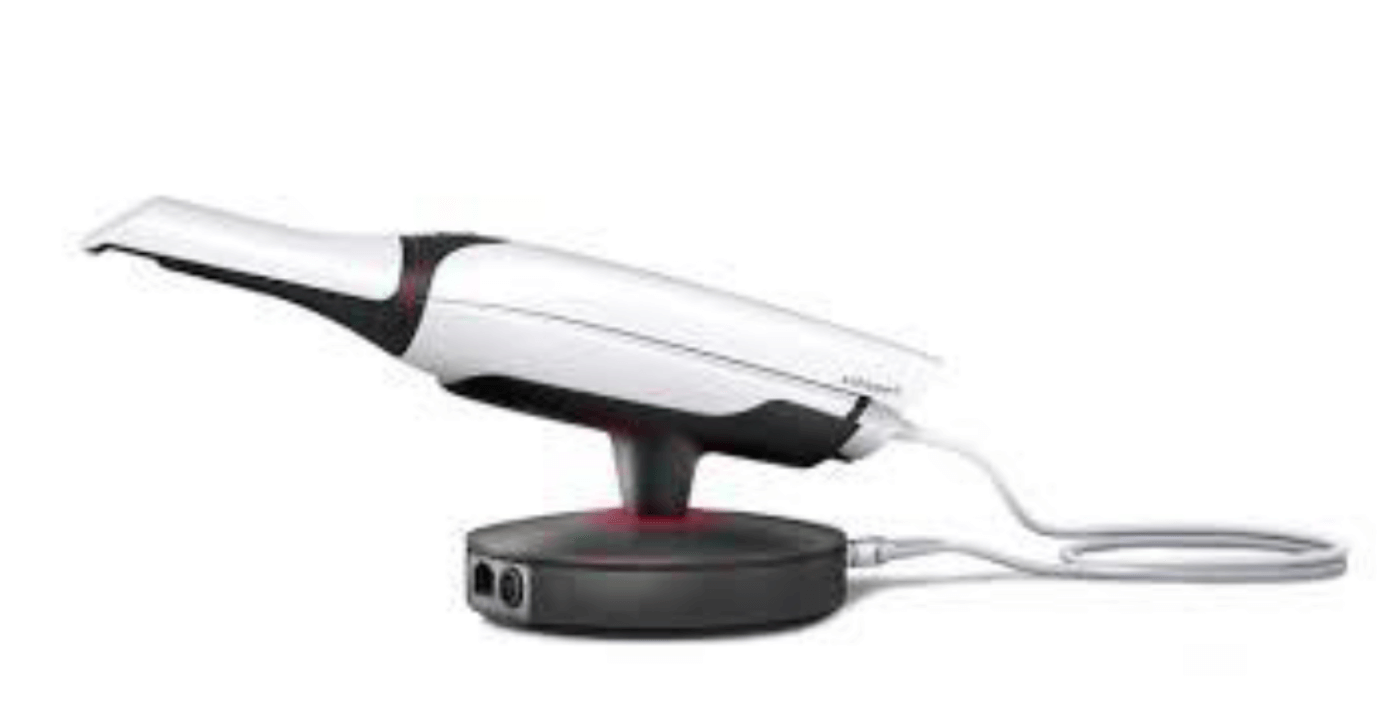
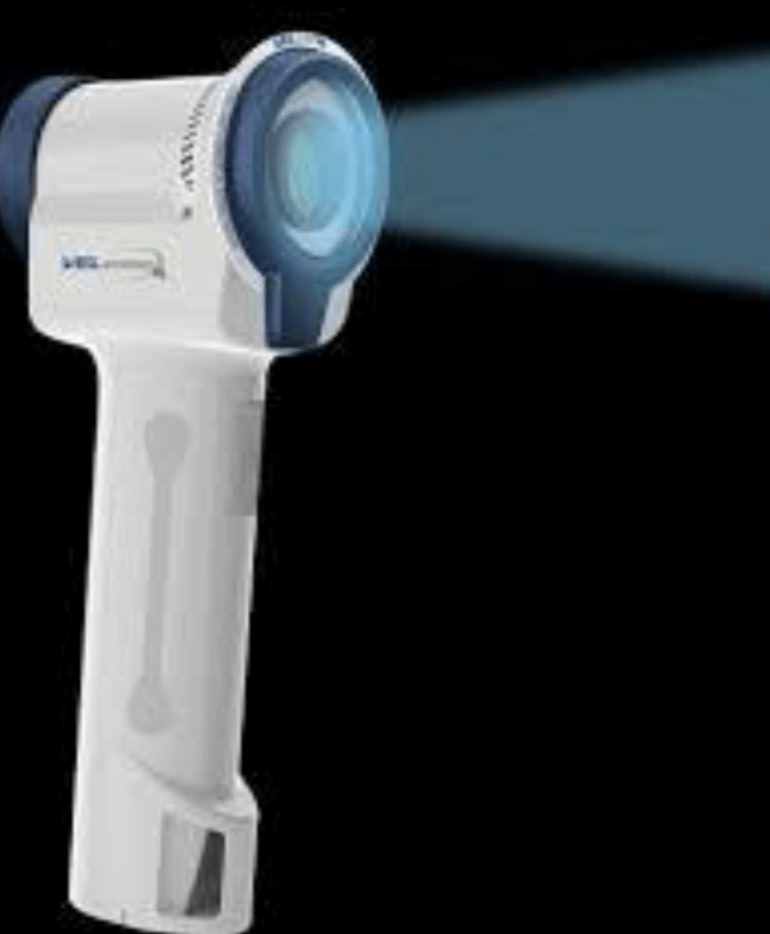
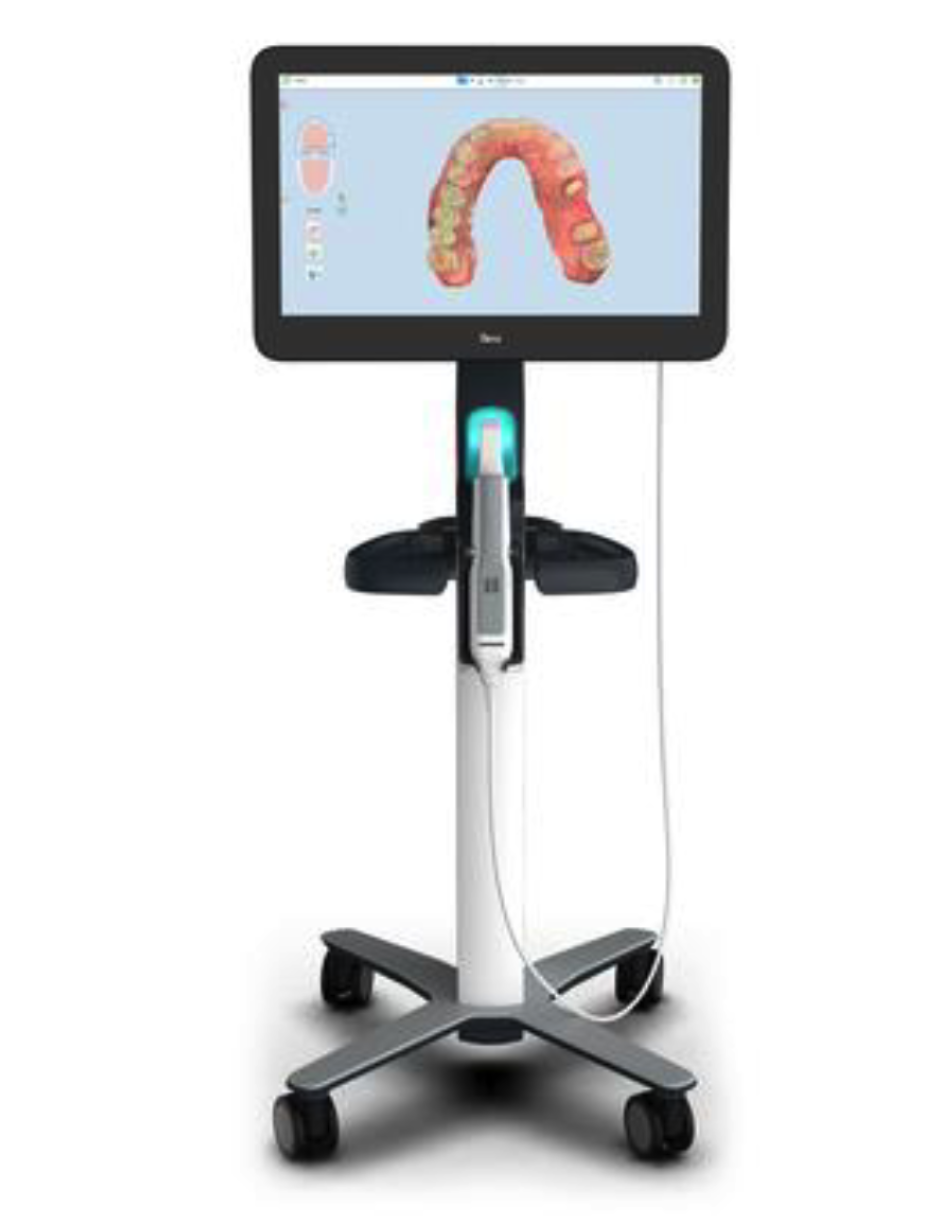
Scanners:
Intraoral scanners have replaced traditional impression techniques, offering a more comfortable experience for patients and delivering precise digital models for treatment planning, including Invisalign and other restorative procedures.
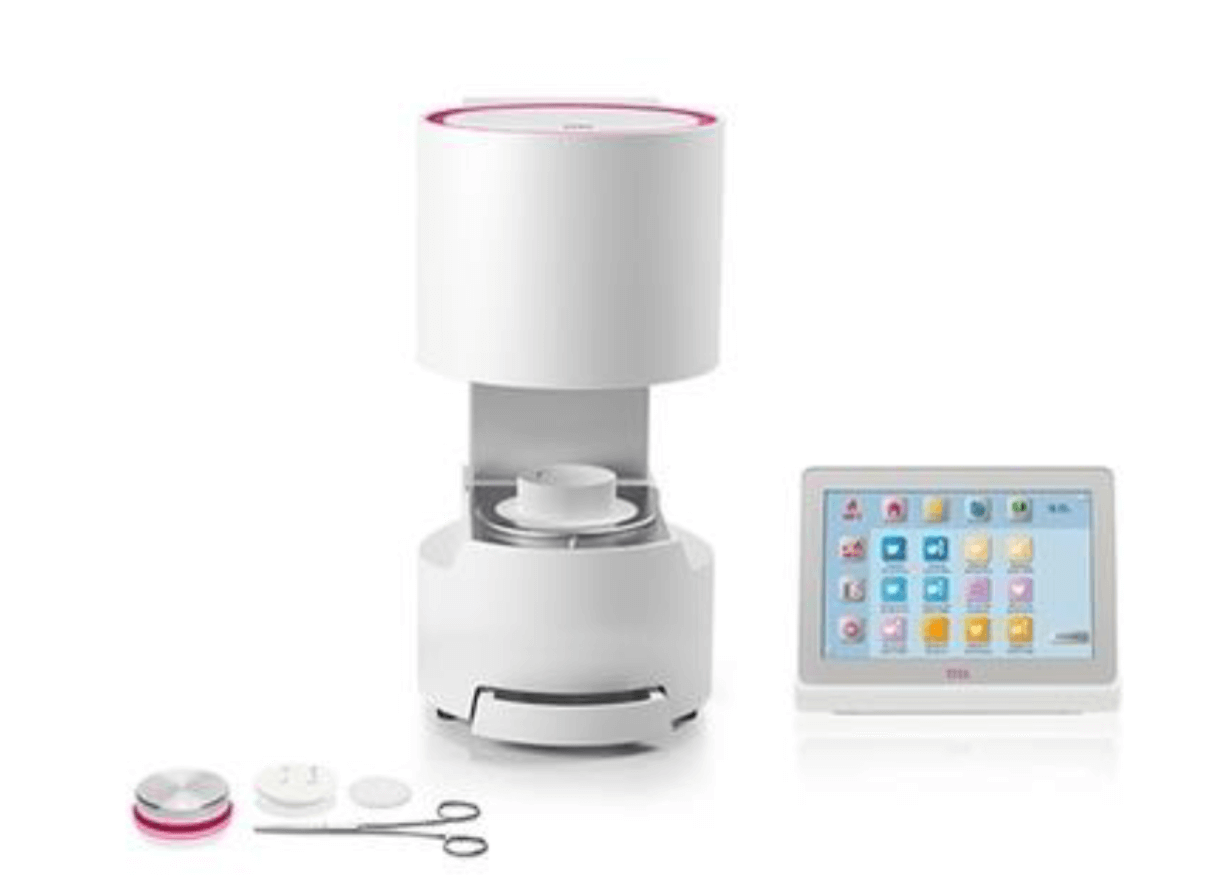
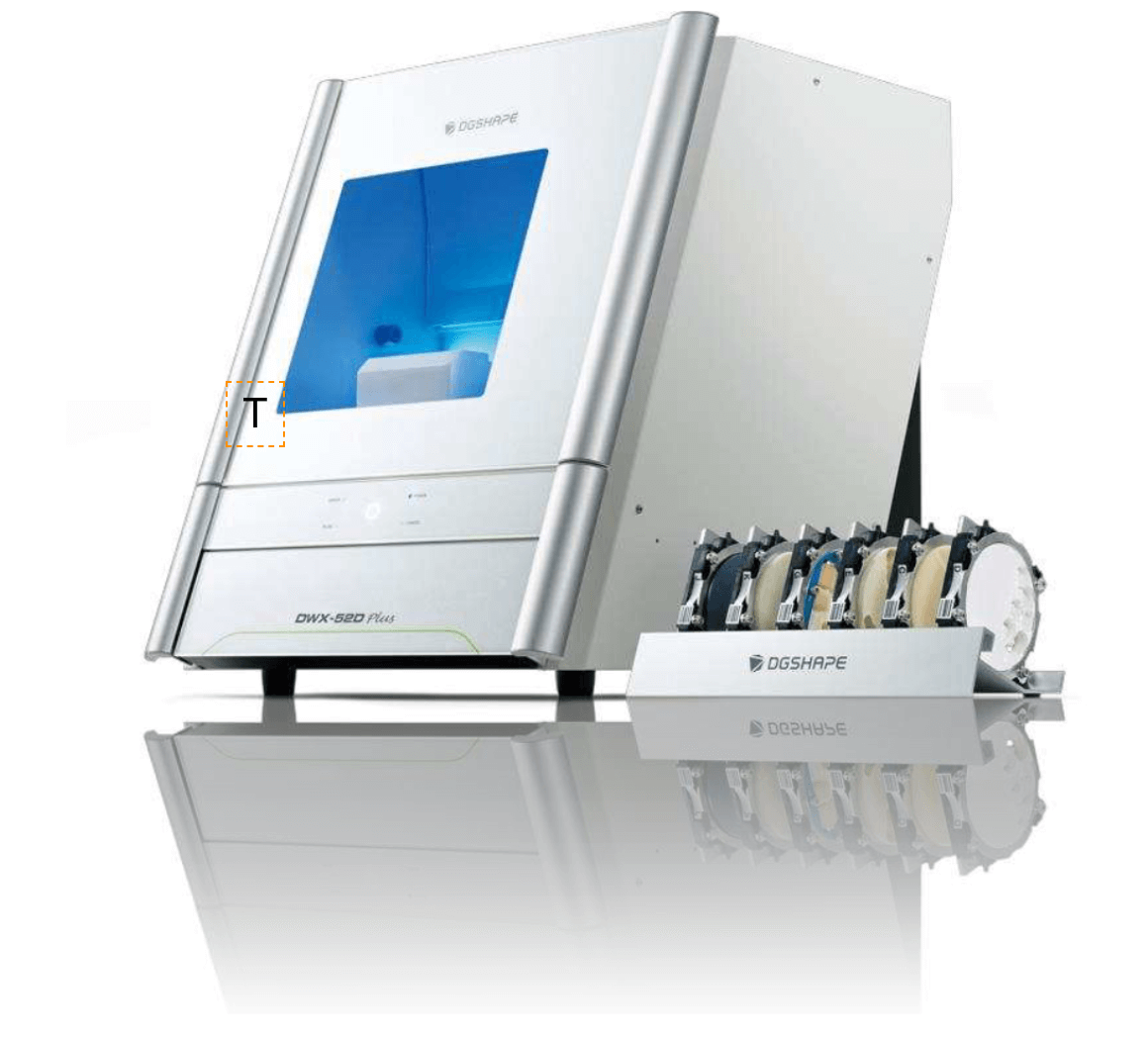
CAD/CAM:
Computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) systems have become indispensable in dentistry, enabling the creation of same-day restorations like crowns and veneers, enhancing efficiency and patient convenience.
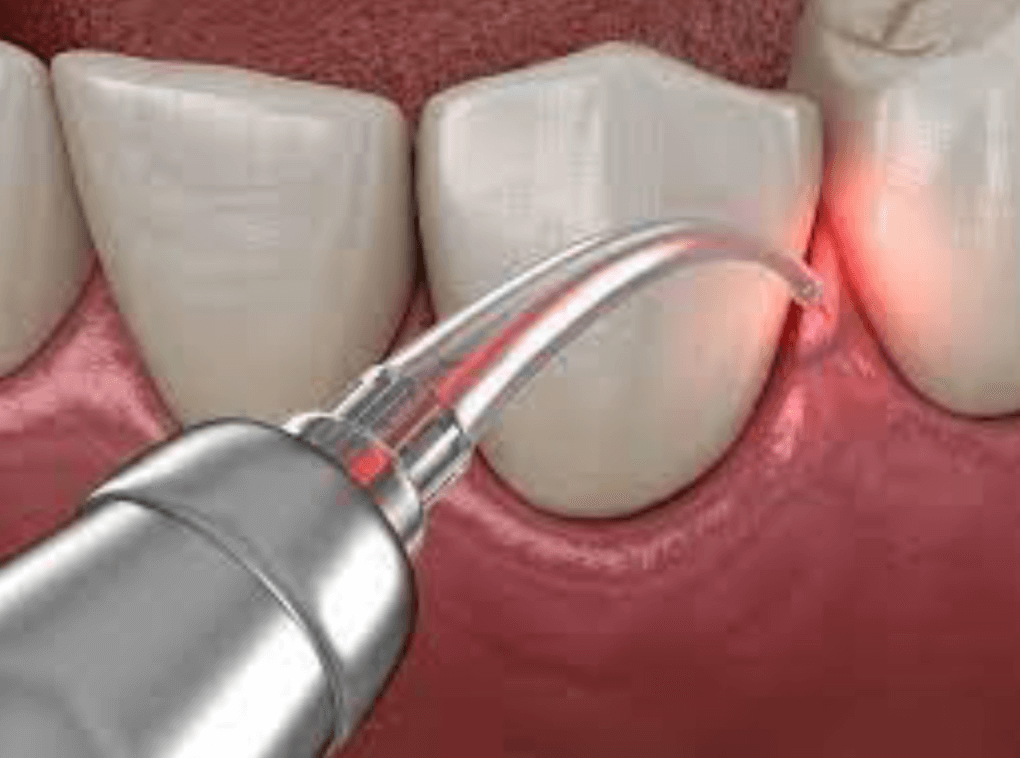
Laser:
Lasers are widely utilized in dental procedures such as cavity removal, gum disease treatment, and teeth whitening. They provide enhanced precision, minimize discomfort, and promote faster healing times.
Teledent:
Telehealth and teledentistry platforms enable remote consultations, monitoring, and follow-ups, improving access to dental care and reaching patients in underserved areas more effectively.
(AI):
Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly being used in dental diagnostics, treatment planning, and patient management. Machine learning algorithms assist in detecting dental issues, analyzing X-rays, and predicting treatment outcomes with greater accuracy.
Robot:
Dental robots are being designed to assist with surgeries, implant placements, and various procedures, enhancing precision and minimizing the margin of error for improved patient outcomes.
Oral Health Apps:
Smart toothbrushes and companion apps empower users to track their oral hygiene routines, providing instant insights and reminders to maintain optimal dental health.
CT Scans:
These devices generate comprehensive 3D visuals of the oral and maxillofacial areas, greatly assisting in intricate procedures like implant placements and orthodontic assessments.
Scaling Devices:
Ultrasonic scalers employ high-frequency vibrations to effectively and comfortably eliminate tartar and plaque from teeth, surpassing the efficiency of traditional scaling techniques.
AR:
Augmented reality can enhance dental education and training by enabling students and professionals to see intricate procedures and anatomical details in real-time.

Biocompatible:
Progress in dental materials has resulted in more resilient and biocompatible solutions, such as tooth-colored fillings and enhanced ceramics for restorations.
Nanotech:
Nanomaterials are being utilized in dentistry for applications like antimicrobial coatings on orthodontic appliances and advanced drug delivery systems for treating dental conditions.
Implant:
Innovations in implant materials and techniques have boosted the success and durability of dental implants, making them a more reliable choice for tooth replacement.